Inflation does not simply affect the unemployment rate but does so in a cyclical fashion where inflation affects unemployment rates and vice versa. However this relationship is more complicated than it appears at first glance and has broken down on a number of occasions over the past 45 years.

Inflation Unemployment And Stabilization Policies Duffka School Of Economics Economics Teaching Economics Economics Lessons
In the long run as price and nominal wages increase the short-run aggregate supply curve moves to SRAS2 and output returns to YP as shown in Panel a.

. The hope is that the bump in rates will increase price of borrowing which could slow business investment to decrease demand and meet supply. This happens when the prices of goods and services decrease. When economists track the performance of the US.
If the unemployment rates were at 6 which is through the fiscal and monetary stimulus the rates would be decreasing by 5 and the impact on the inflation rates would be more negligible We also see that when the unemployment has fallen to a 4 which was from 6 and the inflation rates correspond from a rise of 3 from that which was 1. You may start from AW. But a fall in demand which causes inflation to fall will cause a rise in the inflation rate.
Unemployment and price increase rate when the rate of joblessness was high the rate of inflation was also high and vice versa. During other periods both inflation and unemployment were increasing as from 1973 to 1975 or 1979 to 1981. The Relationship Between Unemployment and Inflation.
In the 20-year of US. The higher the inflation rate the lower is the unemployment level. Thus there exists a trade-off between inflation and unemployment.
Evaluate the historical relationship between unemployment and inflation. Phillipss finding of the relationship between unemployment and inflation Distinguish between the short-run and the long-run in a macroeconomic analysis. In Panel b the unemployment rate will fall to U1 and the inflation rate will be π1.
As levels of unemployment decrease inflation increases. A period of rising inflation and unemployment is called a stagflation phase. A few weeks back economist Larry.
This is known as inflationary gap. Inflation data of unemployment disapprove the short-run on the Phillips curve. The Phillips curve relates the rate of inflation with the rate of unemployment.
The relationship however is not linear. Three years later both the inflation and unemployment rate began to rise in industrialized countries. Second unemployment can also lead to inflation.
What is the relationship between unemployment and inflation. High inflation seems to cause a rise in the unemployment rate. A look at the relationship between inflation and unemployment and whether there is a trade-off as suggested by the Phillips Curve.
One economic model the Phillips Curve suggests that when unemployment is low inflation increases and vice-versa. Expert Answer According to the Phillips curve jobless and boom are inversely relatedThe correlation between low unemployment and higher inflation and high unemployment and lower inflation or even deflation is well documentedFrom a logical point of view this. When unemployment is high the number of people.
Phillips curve suggests as unemployment falls and the economy gets closer to full employment inflation rises. Leave a Comment Inflation By Jonathan Kyle. Discover the Phillips curve graph which shows an inverse dynamic of unemployment and.
This happens when the prices of goods and services increase. This Phillips Curve. For example if there is a 10 inflation rate unemployment will increase by 1.
A fundamental concept in inflation analysis is the relationship between inflation and unemployment called the Phillips curve. We refer to a period when inflation and unemployment are inversely related as a Phillips phase. Why is the relationship between unemployment and inflation different in the short-run and the long-run.
The relationship between inflation and unemployment has traditionally been an inverse correlation. Phillips curve demonstrates the relationship between the rate of inflation with the rate of unemployment in an inverse manner. In Panel b unemployment returns to UP regardless of the rate of inflation.
Economy they pay attention to factors like economic growth inflation and unemployment. If levels of unemployment decrease inflation increases. View the full answer Previous question Next question.
As a result businesses may not be able to afford to pay their employees. A natural rate of unemployment essentially means that inflation has no long-term relation to unemployment. 1- Labor Supply and Demand.
Unemployment can also affect inflation in two ways. Relation between Unemployment and Inflation When we relate this situation with the concept of unemployment then we can say that in case of long run increase in demand will give maximum benefit to the company or the industry when the economy has a starting point when the employment level in the economy is full. First unemployment can lead to deflation.
As mentioned above the relationship between Unemployment and Inflation was initially introduced by AW. In 1968 American economist Milton Friedman suggested that there is no long-term link between inflation and unemployment. Graphically the short-run Phillips curve traces an L-shape when the unemployment rate is on the x-axis and the inflation rate is on the y-axis.
The relationship is negative and not linear. Therefore some level of inflation could be considered desirable to minimize unemployment. But is that always true.
Learn the relationship between unemployment and inflation. The Phillips curve argues that unemployment and inflation are inversely related. The reason being instability in the trade balance between the joblessness and price rises rate.
This model suggests that there is a trade-off between price stability and employment. The nature of the relationship between inflation and unemployment has implications for the appropriate conduct of monetary policy. However the question as to whether the traditional Phillips curve relationship holds true remains debatable despite advances in both theoretical and empirical evidence.

Concentration Ratio Vs Herfindahl Hirschman Index Market Structure Microeconomics Basic Concepts Sales And Marketing Concentration

Ap Classroom Classroom Chart Quiz

Substituting Income Annuities For Bond Funds In Retirement Bond Funds Annuity Financial Asset

Pin By Lean Todayy On Saas Girisimplus Economics Lessons Teaching Economics Economics Notes

Ap Macroeconomics Review Every Graph You Need To Know For The Exam Youtube Macroeconomics Teaching Economics Learn Economics

How To Calculate Growth Rate Growth Calculator Rate

Pareto Efficiency No One Can Be Made Better Off Without Making At Least One Individual Worse Off Given An Initial Allocation Of Goods Amo Finansy Ekonomika

Inflation In America In 2022 Wonder Tax Breaks Small Business

Ap Classroom Classroom Chart Quiz

For A Yellen Fed Smooth Transition Will Be Tall Order Global Economy Financial Markets Economy

Difference Between Perfect Competition Efficient Market Hypothesis Teaching Economics

Production Possibility Frontier Tutor2u Economics Economics Lessons Teaching Economics Economics

The Trade War Between The Usa And The People S Republic Of China People S Republic Of China War Trading
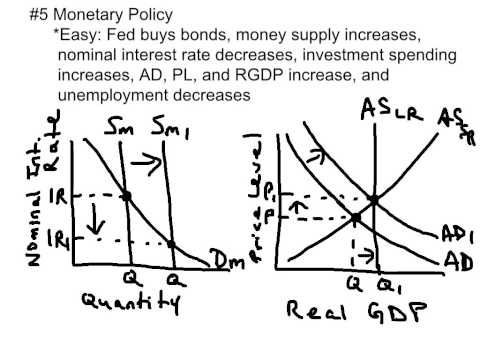
Top 10 Ap Macroeconomics Exam Concepts To Know Youtube Macroeconomics Economics Lessons Economics